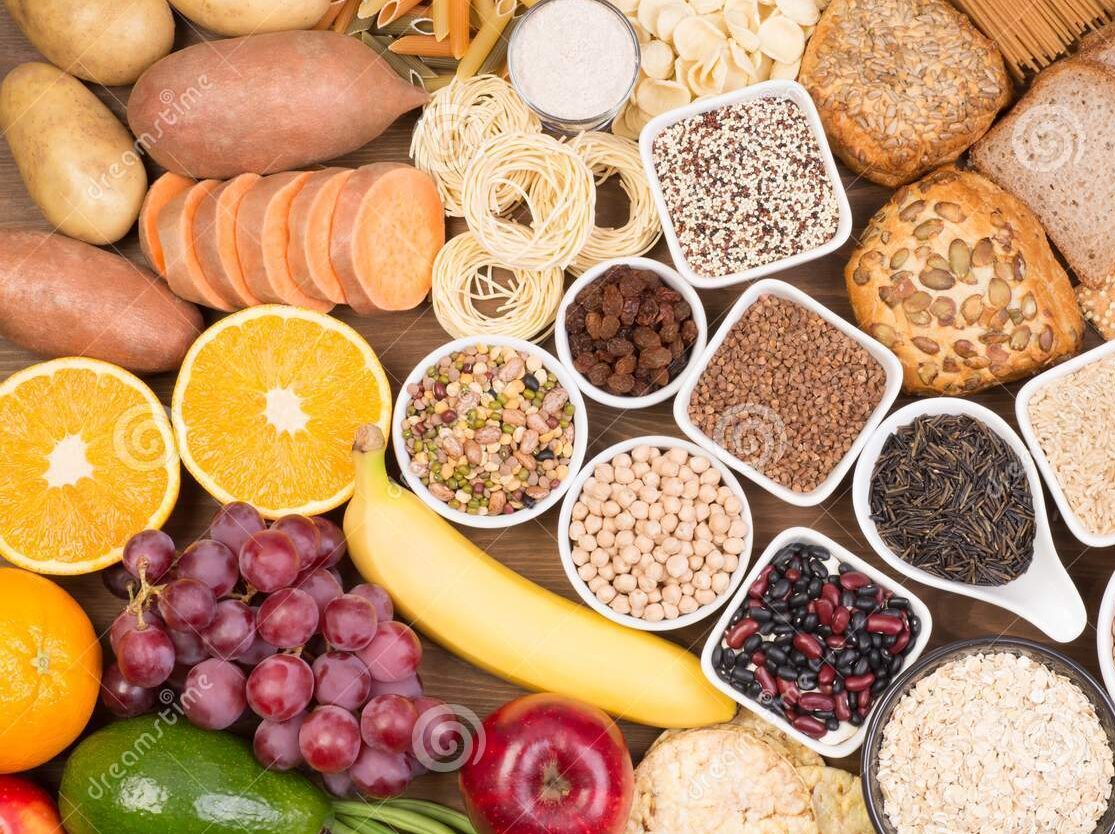
Carbs as one of the macro-nutrients is widely discussed in the nutrition world. This article covers their primary information, types, functions and sources.

Source: Dreamstime
WHAT ARE CARBS?
Carbohydrates are one of three macro-nutrients that your body requires on a daily basis, along with proteins and fats. These are biological compounds and have certain ratios of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
At their most basic, building blocks of sugars make up carbohydrates. The number of sugar units grouped in each molecule classify them. Glucose, fructose and galactose are examples of single-unit sugars. Sucrose and lactose are widely known double-unit sugars.
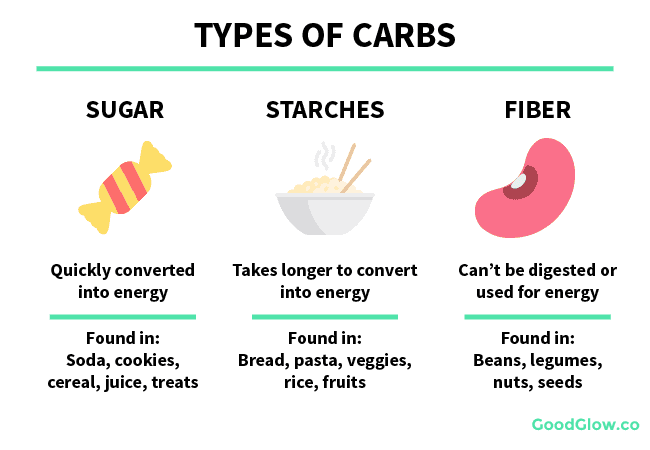
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT TYPES ?
Carbs are distinguished into Simple and Complex forms. Various types are as follows :
- SUGAR – Sugar falls in the category of Simple Carbohydrates. This is because they are in the most basic form. Fruits and vegetables are natural sources of sugar. Additionally, Processed foods and desserts are the artificial sources.
- STARCH – This is a Complex carbohydrate. Simple sugars stick together to form complex carbs. Body processes starch by breaking them into sugars. Pasta, bread and cereals are some of its sources.
- FIBER – Fiber is also a complex carbohydrate. But unlike starch, body cannot break these down. It generally passes through the body undigested. So, eating foods with fiber can help you feel full and make you less likely to overeat.Foods that come from plants, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, beans, and whole grains are rich in Fiber.
Source: GoodGlow.co
WHAT ARE THE SOURCES OF CARBS?
Healthy sources of carbohydrate include –
- Whole grains: quinoa, amaranth, barley, brown rice, oatmeal, whole-grain pasta and whole-grain breakfast cereals
- Fruits: berries, citrus fruits, melons, apples, pears, bananas and kiwifruit
- Starchy vegetables: sweet potatoes, yams, corn. peas and carrots
- Legumes: lentils, black beans, pinto beans, navy beans, chick peas and soybeans
- Milk products: low-fat milk, plain yogurt and soy yogurt
- Non-starchy vegetables: leafy greens, spinach, cabbage, asparagus, tomatoes, broccoli, cauliflower, green beans, cucumbers, peppers, zucchini and mushrooms
- Nuts and seeds: pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, almonds, cashews, walnuts, peanuts and pistachios
- Soy milk and tofu
HOW DOES BODY REACT TO THESE FOODS?
Body breaks carbohydrates into glucose i.e., the single unit sugars. It does this to generate energy to perform bodily functions. This is also quick, steady and instant source of energy without extra supplement. Additionally, it not only produces energy but also reserves it. It stores energy in muscles and liver and uses it when essential.
WHAT ARE THE FUNCTIONS OF CARBS IN YOUR BODY?
- ENERGY SOURCE – The primary role of carbohydrates is to supply energy to all cells in the body. Many cells prefer glucose as a source of energy versus other compounds like fatty acids. Some cells, such as red blood cells, are only able to produce cellular energy from glucose.Cells that require energy remove the glucose from the blood with a transport protein in their membranes. The energy from glucose comes from the chemical bonds between the carbon atoms. Cells in our bodies break these bonds and capture the energy.
- ENERGY RESERVE – When the body already has enough energy to support its functions, it stores extra glucose as Glycogen. Our muscles and liver hold the majority of this reserve. There are an excess of fifty thousand single glucose units in a a molecule of glycogen. These are highly branched. This allows for the rapid flow of glucose when it is needed to make cellular energy.
- MACRO-MOLECULES – Body absorbs most of the glucose as energy. But it converts some of it into ribose and deoxyribose. These are the building blocks of important macro-molecules of our body. These include RNA, DNA & ATP.
- GUT HEALTH – Body cannot break complex carbs like Fiber. But it still plays a role in promoting gut health. It does this by increasing the physical bulk in the bowel, and thereby stimulating the intestinal transit.
- LIPID METABOLISM – Lipid is an important component of cell. As blood-glucose levels rise, the use of lipids as an energy source is inhibited. Thus, glucose additionally has a “fat-sparing” effect. This is because an increase in blood glucose stimulates release of the hormone insulin, which tells cells to use glucose (instead of lipids) to make energy.

